A complete list of our publications is available on Google Scholar, please find below our highlighted work (we strongly support Open Access).
2025
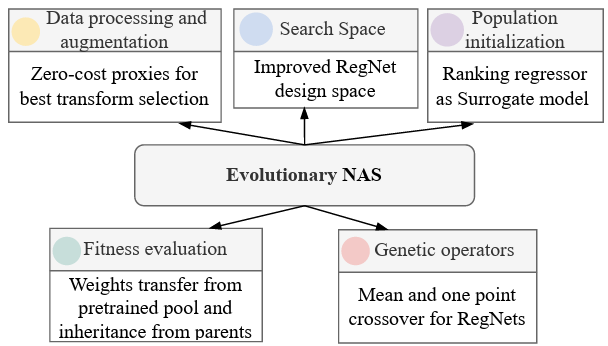
Pava, M. A., Groh, R., & Kist, A. M (2025). EG-ENAS: Efficient and Generalizable Evolutionary Neural Architecture Search for Image Classification. In AutoML 2025 Methods Track.
Article / Code
We propose an efficient evolutionary NAS framework with dataset-aware augmentation selection, improved RegNetY search space, a regressor for population initialization, and a stage transfer method, achieving good generalization across eleven datasets.
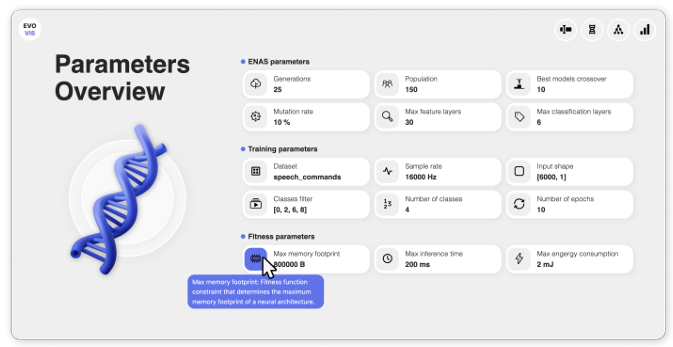
Dang, L., Groh, R., & Kist, A. M. (2025). EvoVis: Dashboard for Visualizing Evolutionary Neural Architecture Search Algorithms. Journal of Open Source Software, 10(111), 7728.
Article / Code
Evolutionary Neural Architecture Search contains and produces a high amount of meta information. Lea Dang developed a novel dashboard, EvoVis, that allows easy access to and investigation of this information.
Kist, A. M. and Döllinger, M. (2025). Have We Solved Glottis Segmentation? Review and Commentary. J Voice 39(3), 574-576.
Article / PDF
Quantifying vocal fold oscillation is a key task in High-Speed Videoendoscopy (HSV), and glottis segmentation is a crucial step. Here, we review whether fully automatic glottis segmentation has been solved with the advent of deep learning or if there are any open questions to address in the future.
2024
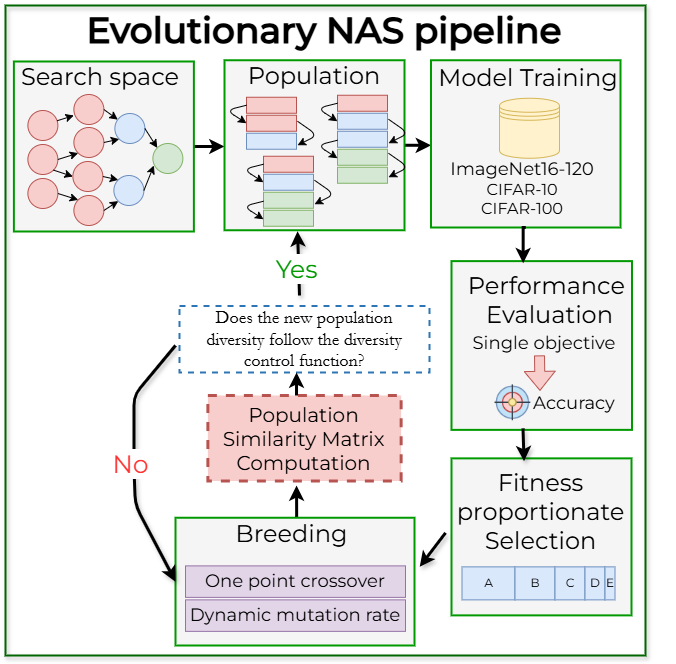
Pava, M. A.; Groh, R.; Kist, A. M. (2024, Sep); Sequence Alignment-based Similarity Metric in Evolutionary Neural Architecture Search – Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Automated Machine Learning, PMLR 256:8/1-21
Article / Code
Neural Architecture Search (NAS) has emerged as a powerful method for automating the design of deep neural networks across diverse applications, with evolutionary optimization showing particular promise in addressing its intricate demands. However, the effectiveness of this approach highly depends on balancing exploration and exploitation, ensuring that the search does not prematurely converge to suboptimal solutions while still achieving near-optimal outcomes. This paper addresses this challenge by proposing a novel similarity metric inspired by global sequence alignment from biology. Experimental results conducted on popular datasets for image classification, such as CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and ImageNet16-120, show the effectiveness of our approach in guiding diversity based on our suggested control function.
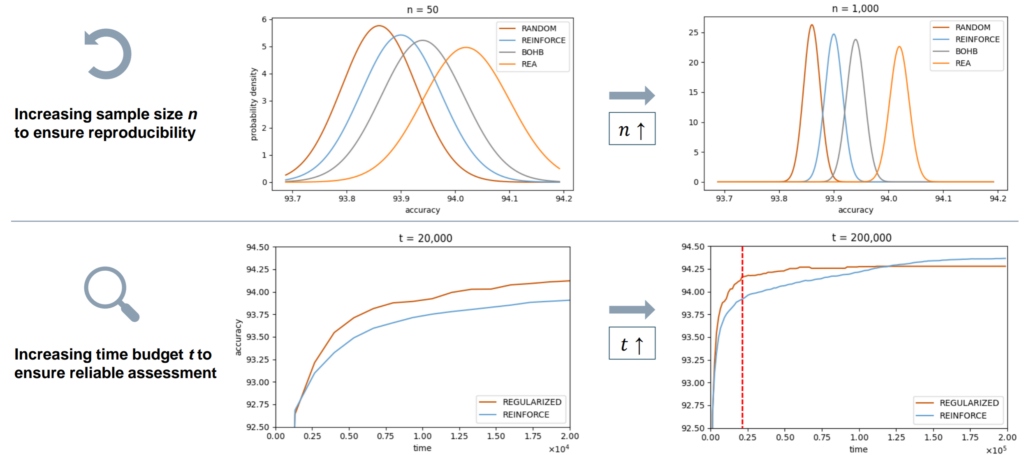
Dendorfer, S., Kist, A. M. (2024). Beyond the Threshold: Time Is All You Need – AutoML Conference 2024 (Workshop Track)
Article / PDF / Code / Video
This paper addresses statistical misuse in neural architecture search (NAS) on tabular benchmarks, focusing on sample size and time constraints. We recommend using at least 1000 runs for reliable comparisons and sufficient time budgets until convergence. Our findings advocate for more robust statistical practices to enhance NAS research reliability and reproducibility.

Groh, R., Li, J. Y., Li-Jessen, N. Y., & Kist, A. M. (2024). ANNOTE: Annotation of time-series events. Software Impacts.
Article / Code
Here, we present a new annotation software, Annotation of Time-series Events (ANNOTE), to handle longitudinal, time-series signals as in highly complex physiological events. ANNOTE offers flexibility and adaptability to streamline the annotation process through an intuitive user interface, effectively meeting diverse annotation needs. Users can annotate regions of interest with precision down to a single data point. ANNOTE presents a useful tool to support researchers in handling time-series biomedical data for downstream machine-learning analyses.

Rodríguez, B. L.*, Borges, G. L.*, García, M. L. B*., Schützenberger, A., & Kist, A. M. (2024, May). Neural Radiance Fields for 3D Reconstruction in Monoscopic Laryngeal Endoscopy. In 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI).
*these authors contributed equally – publication from our BIMAP seminar!
Article / PDF (avoid the paywall)
Laryngeal endoscopy is typically performed with a monoscopic endoscope, limiting the exploration to 2D. In this work, we show for the first time how to reconstruct the larynx from endoscopic footage with unknown depth information.
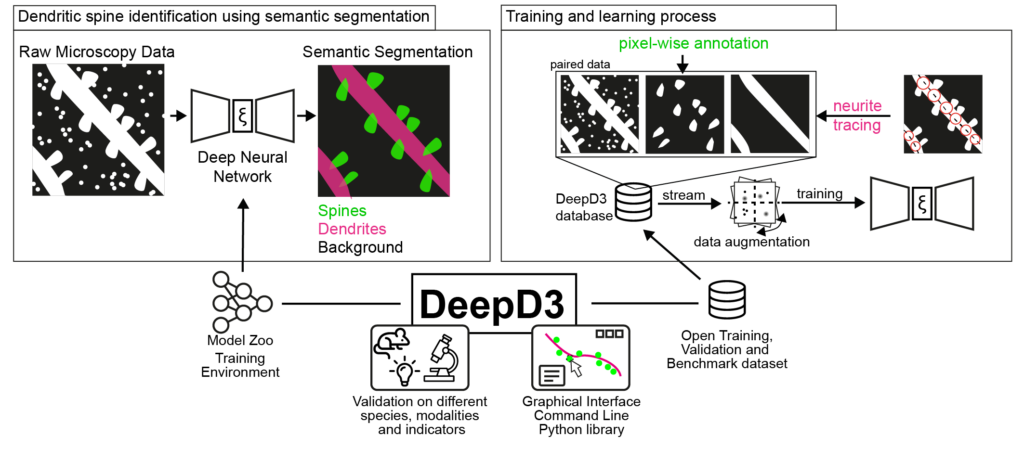
Fernholz, M.H.P., Guggiana Nilo, D. A., Bonhoeffer, T., Kist, A. M. (2024). DeepD3, an open framework for automated quantification of dendritic spines – PLOS Computational Biology
Article / Code / Datasets / Model Zoo / Contribute
This work tackles the automated quantification of a crucial structure in the brain: dendritic spines, critical to many functions of the brain such as learning and memory. We introduce DeepD3, an open-source tool that uses deep learning to automatically and accurately quantify dendritic spines. Trained on a diverse range of data, annotated by multiple experts under various experimental conditions, DeepD3 is not only efficient and reliable but also transparent and adaptable to different research needs.
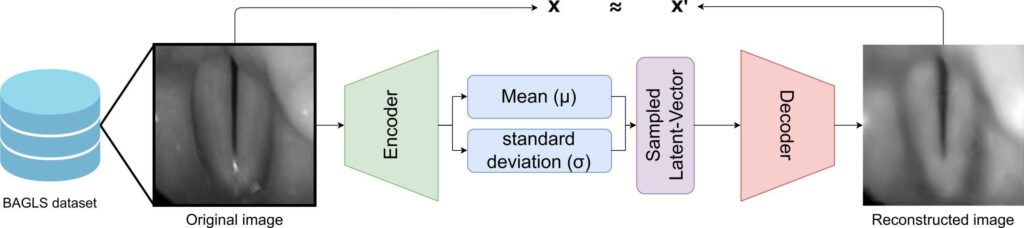
Darvish, M. & Kist, A. M. (2024). A Generative Method for a Laryngeal Biosignal – Journal of Voice
Article / GIF
We introduce a new method that uses Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) to create synthetic endoscopic footage that closely resemble real ones, providing a useful resource for researchers and clinicians. We further show that using a vector describing the glottis opening (glottal opening vector, GIOVe) we can arbitrary close and open the glottis while maintaining the overall laryngeal anatomy. With that, we show that we can create artificially glottal area waveforms of any given frequency.
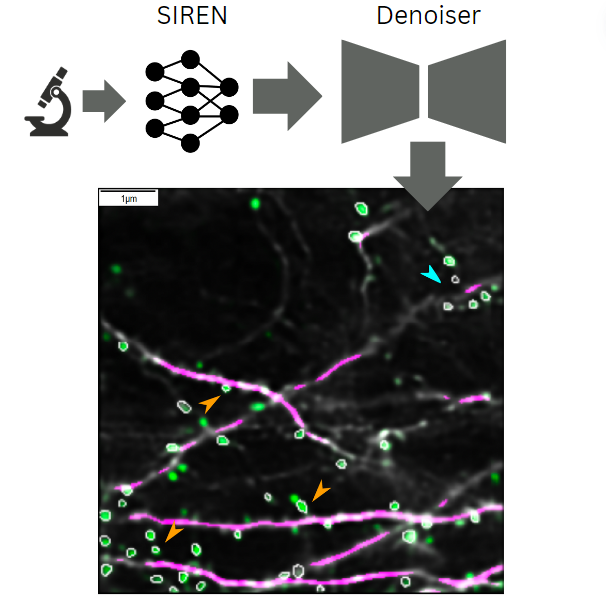
Hauser, S.L., Brosig, J., Murthy, B., Attardo, A. ,Kist, A. M. (2024). Implicit neural representations in light microscopy – Biomedical Optics Express.
Article
In this work, we explore the use of implicit neural representations in light microscopy using the SIREN networks introduced by Sitzmann et al.. Here, we use SIRENs (MLPs with sine activation functions) to predict intermediate planes across multiple micrometers and automatically correct motion artifacts while denoising images. Although SIRENs can affect noise statistics, this issue is mitigated using a denoising neural network, as demonstrated by the recovery of dendritic spines.

Groh, R., Goes, N. & Kist, A. M. (2024). SpokeN-100: A Cross-Lingual Benchmarking Dataset for The Classification of Spoken Numbers in Different Languages. TinyML Research Symposium.
Article / Code / Data
This study introduces a novel, entirely artificially generated benchmarking dataset tailored for speech recognition, representing a core challenge in the field of tiny deep learning. SpokeN-100 consists of spoken numbers from 0 to 99 spoken by 32 different speakers in four different languages, namely English, Mandarin, German and French, resulting in 12,800 audio samples.
2023

Dörrich, M., Hecht, M., Fietkau, R., Hartmann, A., Iro, H., Gostian, A. O., … & Kist, A. M. (2023). Explainable convolutional neural networks for assessing head and neck cancer histopathology. Diagnostic Pathology, 18(1), 121.
Article
In this paper, we investigate Convolutional Neural Networks for classification and semantic segmentation of head and neck cancer histopathology. Using Explainable AI, we show that the networks not only achieve high accuracy in predicting tumor tissue but also rely on features that align with the expert opinion of pathologists.
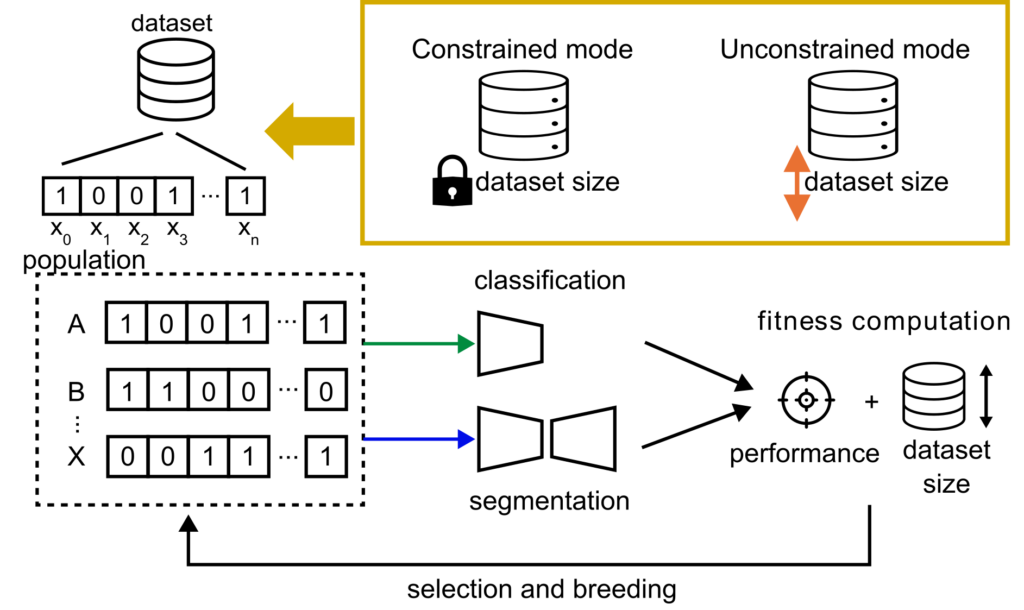
Neubig, L., Kist, A.M. (2023). Dataset Pruning using Evolutionary Optimization. Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2023.
Article
The right number of data points to solve an image processing task is crucial. To analyze how many data points in a dataset are important and unique enough to support the learning process of a neural network, we used an evolutionary approach in constrained (fixed dataset size) and an unconstrained mode (flexible dataset size).
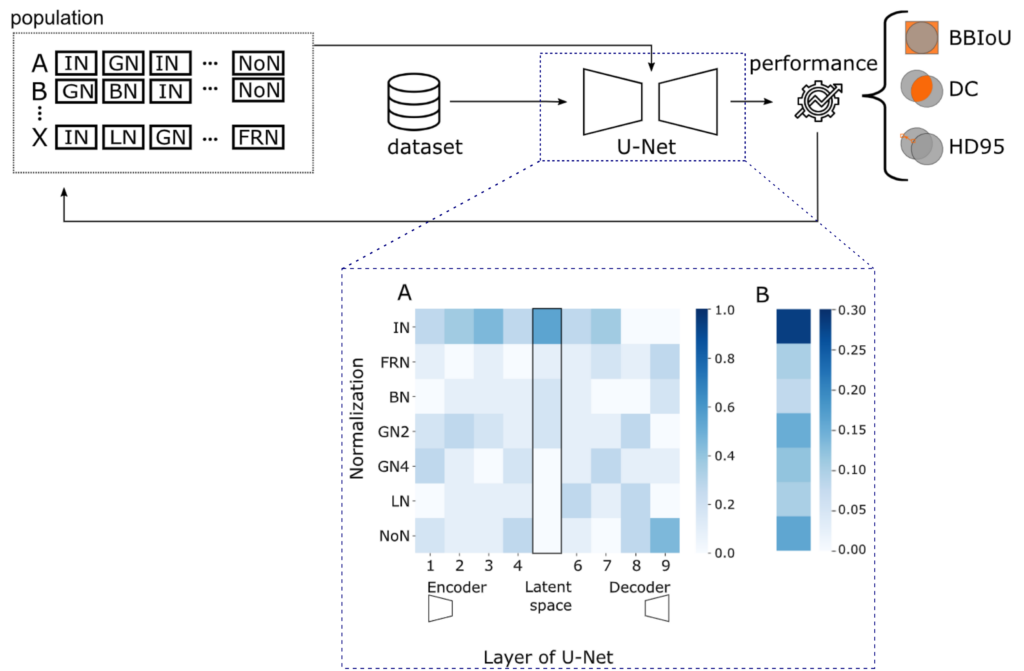
Neubig, L., Kist, A.M.(2023). Evolutionary Normalization Optimization Boosts Semantic Segmentation Network Performance. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2023.
Article / Code
Is Batch Normalization always the best normalization method for a medical image segmentation task? We analyzed the influence of normalization methods in a U-Net layer-wise in a systematic study using evolutionary optimization and compared it to state-of-the-art models.

Groh, R. & Kist, A. M. (2023). End-to-end evolutionary neural architecture search for microcontroller units. IEEE COINS.
Article
Here, we introduce our end-to-end evolutionary NAS (EvoNAS) for microcontroller units that optimize both, pre-processing and neural network architectures. Each neural network architecture is assessed using the multi-objective accuracy, memory footprint, inference time, and energy consumption, to derive a common performance measure to be maximized. To ensure immediate use of all potential solutions on the microcontroller environment, we create a software-hardware chain in which each neural network is deployed to measure the inference time and power consumption directly.
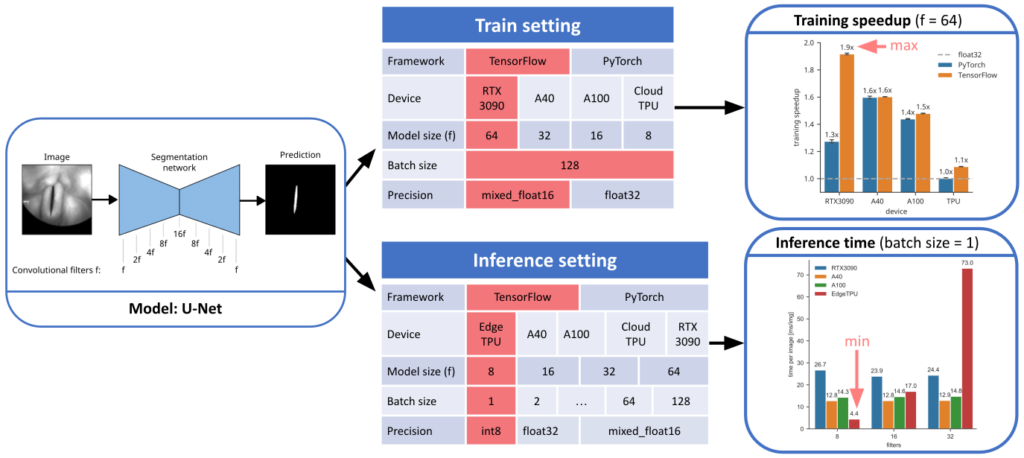
Dörrich, M., Fan, M., & Kist, A. M. (2023). Impact of Mixed Precision Techniques on Training and Inference Efficiency of Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Access.
Article
Our brain works with fuzzy and low-precision logic. In this study, we investigate how mixed-precision techniques have an effect of the training and inference efficiency of encoder-decoder deep neural networks in a biomedical image segmentation task.
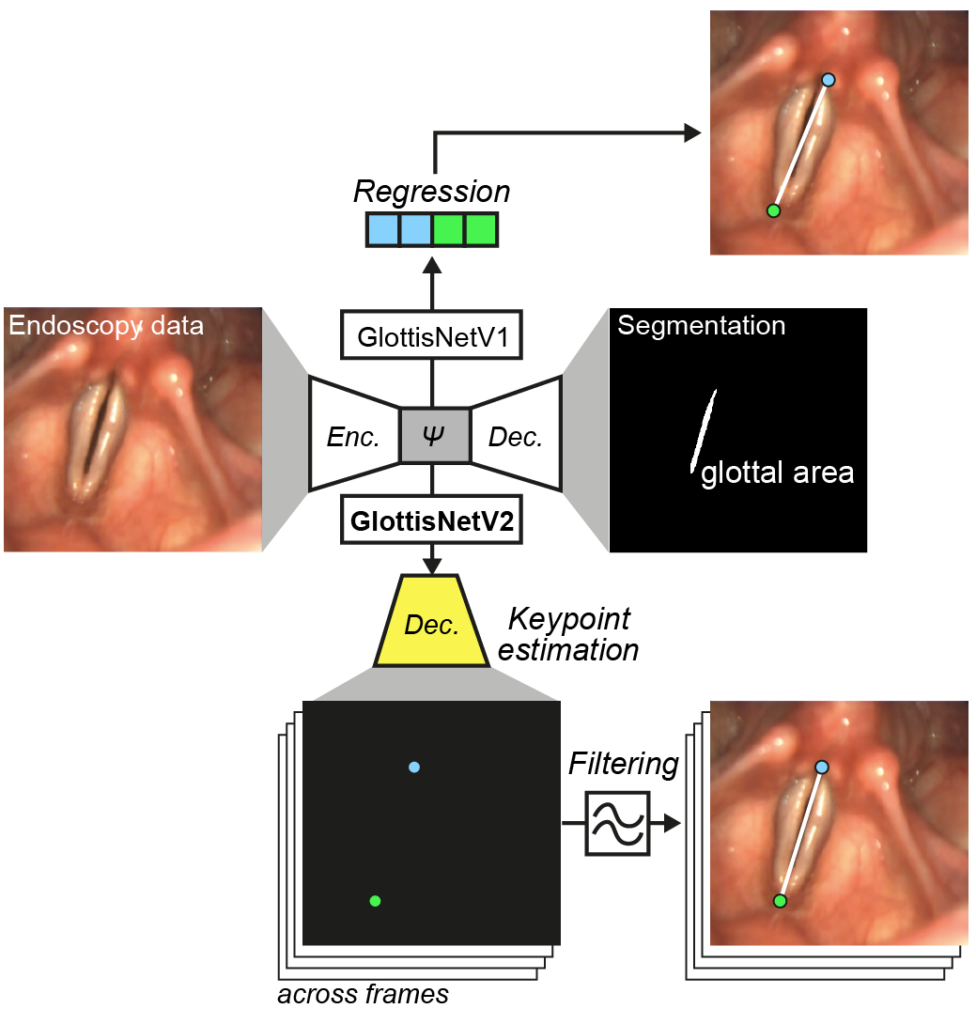
Kruse, E., Döllinger, M., Schützenberger, A., & Kist, A. M. (2023). GlottisNetV2: Temporal Glottal Midline Detection using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine.
Article / Code
Detecting the glottal midline accurately is crucial to assess quantitative parameters related to the symmetrical oscillation of the vocal folds. Here, we show how to use engineered neural networks to allow accurate midline detection simultaneously with glottal area segmentation.
2022

Kist, A. M., Breininger, K., Dörrich, M., Dürr, S., Schützenberger, A., & Semmler, M. (2022). A single latent channel is sufficient for biomedical glottis segmentation. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 14292.
Article / Code / Data
In this paper, we show by mining an encoder-decoder deep neural network that a single latent channel image is sufficient for glottis segmentation. Further, we describe the function of the latent channel and how this affects downstream glottis segmentation.

Groh, R., Lei, Z., Martignetti, L., Li-Jessen, N. Y., & Kist, A. M. (2022). Efficient and Explainable Deep Neural Networks for Airway Symptom Detection in Support of Wearable Health Technology. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2100284.
Article / Code
Airway symptom detection is crucial for monitoring chronic airway-related diseases. In this work, René is showing how data from neck surface accelerometers can be analyzed using a deep neural network in a computational constrained environment. He uses evolutionary neural architecture search to find an accurate, yet fast and deployable deep neural network for wearables.

Neubig, L., Groh, R., Kunduk, M., Larsen, D., Leonard, R., & Kist, A. M. (2022). Efficient Patient Orientation Detection in Videofluoroscopy Swallowing Studies. In Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2022 (pp. 129-134). Springer Vieweg, Wiesbaden.
Article
Swallowing disorders are commonly examined using videofluoroscopy swallowing studies (VFSS). To comprehensively evaluate the swallowing process, a typical VFSS contains different patient orientations. Here, we show a systematic architectural scaling approach and found that an efficient ResNet18 variant is sufficient to classify a full VFSS recording of about 1800 frames in less than 14 s on conventional CPUs.
2021

Kist, A. M., Dürr S, Schützenberger A, and Döllinger M. OpenHSV: An open platform for laryngeal high-speed videoendoscopy. Scientific reports, 11 (2021), 13760.
Article / Code / Docs / Award
Commercially available systems for laryngeal high-speed videoendoscopy have not been further developed lately, are closed-source, and have only very limited analysis capacities. With OpenHSV, we provide a novel, award-winning, open hard- and software platform with DNN-powered online analysis.
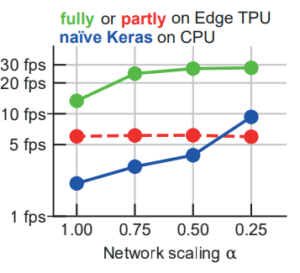
Kist, A. M., and Michael Döllinger. Efficient biomedical image segmentation on Edge TPUs. Accepted as a short paper at Medical Imaging with Deep Learning (MIDL), 2021
Article
We highlight at MIDL our work on semantic segmentation using Edge TPUs.
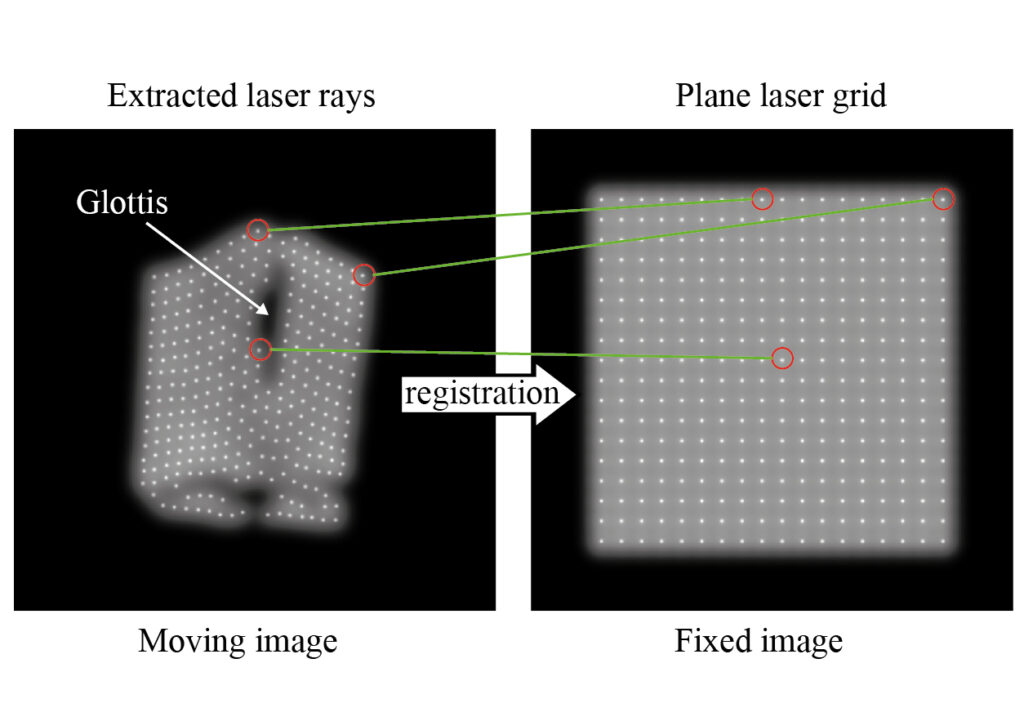
Kist, A. M., Zilker J., Döllinger M., & Semmler M. Feature-based image registration in structured light endoscopy. Accepted as full paper at Medical Imaging with Deep Learning (MIDL), 2021
Article / Code
Structured light endoscopy is a 3D-imaging method. However, the assignment of a projected laser grid to its reference is still tricky. We propose a Deep Learning-based image registration approach that achieves 91% accuracy on an ex vivo dataset.
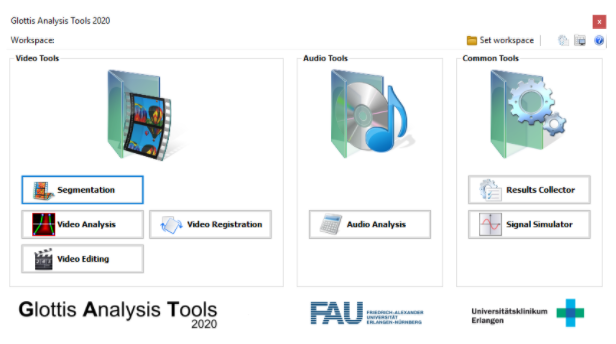
Kist, A. M., Gómez P., Dubrovskiy D., Schlegel O., Kunduk M., Echternach M., Patel RR., Semmler M., Bohr C., Dürr S., Schützenberger A., & Döllinger M. A Deep Learning Enhanced Novel Software Tool for Laryngeal Dynamics Analysis. J Speech Lang Hear R, 64 (6), 1889-1903.
Article
The analysis of high-speed videoendoscopy data is crucial for voice quantification. In this paper, we describe the Glottis Analysis Tools (GAT). GAT has been actively developed in C# since 2010 and is used by dozens of labs worldwide.
2020

Kist, A. M., and Michael Döllinger. Efficient Biomedical Image Segmentation on EdgeTPUs at Point of Care. IEEE Access 8 (2020): 139356-139366.
Article
Deep neural networks are changing the way of biomedical diagnosis. For image segmentation, they can be very large and slow, especially on CPUs. In our recent study, we show that we can improve the glottis segmentation inference speed >79x fold by optimizing a popular biomedical segmentation network (U-Net) and porting it to the inexpensive EdgeTPU Hardware Accelerator.

Kist, A. M., Zilker, J., Gómez, P., Schützenberger, A., & Döllinger, M. (2020). Rethinking glottal midline detection. Scientific reports, 10(1), 1-15.
Article / Code
Symmetry is important in vocal fold motion. The identification of the glottal midline is crucial to deriving symmetry from the glottal area. Here, we evaluate different approaches to determine the glottal midline and suggest a multi-task architecture, GlottisNet, that predicts both simultaneously, glottis segmentation and glottal midline.

Gómez, P.*, Kist, A. M.*, Schlegel, P., Berry, D. A., Chhetri, D. K., Dürr, S., … & Döllinger, M. (2020). BAGLS, a multihospital benchmark for automatic glottis segmentation. Scientific data, 7(1), 1-12.
Article / Code / Dataset
Glottis segmentation is a key component for analyzing the vocal fold vibrations. With BAGLS, we provide the first open, multihospital dataset for training and evaluating deep neural networks.
2019
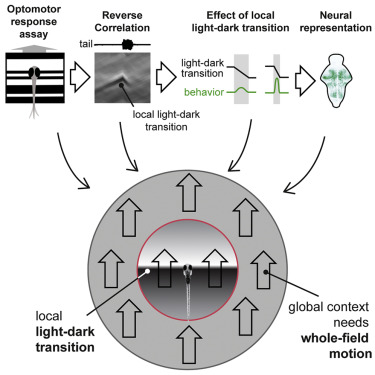
Kist, A. M., & Portugues, R. (2019). Optomotor swimming in larval zebrafish is driven by global whole-field visual motion and local light-dark transitions. Cell Reports, 29(3), 659-670.
Article
Larval zebrafish swim when they perceive a whole-field moving stimulus. However, the underlying features that drive optomotor swimming remain elusive. Here, we show that larval zebrafish are predominantly driven by local light-dark transitions.